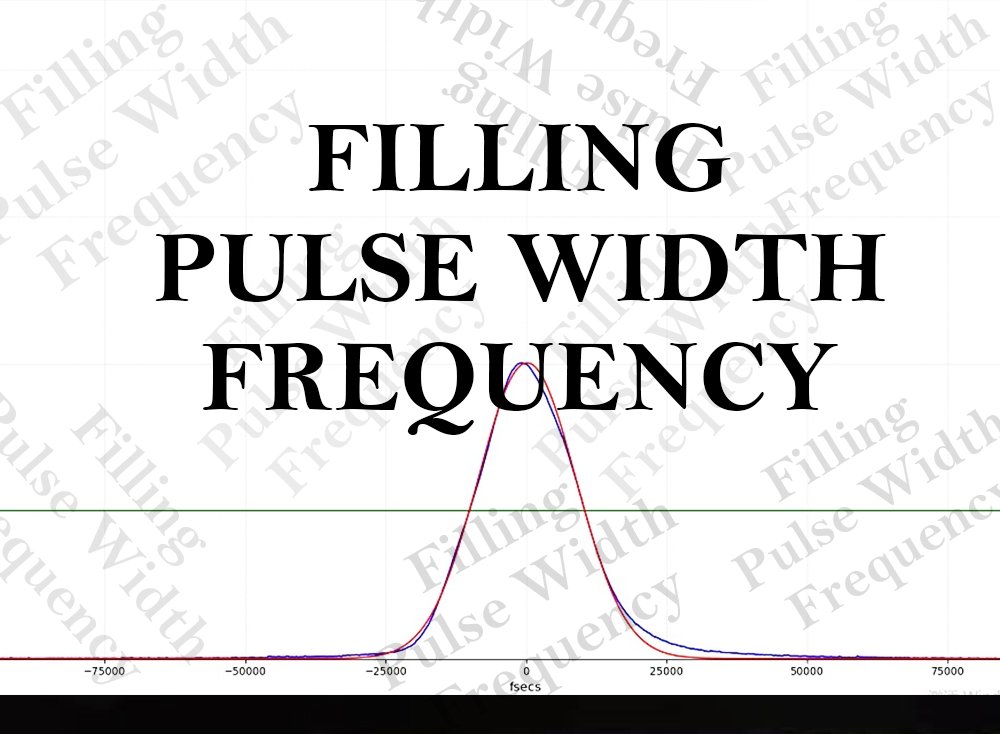
When using a laser marking machine to engrave text or graphics, there are three commonly adjustment parameters: filling, frequency, and pulse width in EzCad marking software. What is the correlation between these three parameters? How do these three parameters affect the laser engraving effect ?
1. What's the FILLING ?
Filling is the laser walking path during engraving, which is used to indicate the position and direction. Filling generally affects the energy distribution of processing. Due to the different characteristics of lasers, the actual line width of the processing effect will be thicker than the filling line. In the actual laser engraving, each line is composed of countless points. Each point is the result of the energy of a laser pulse. By modifying the pulse width, different energies can be obtained.

2. What's the PULSE WIDTH ?
Pulse width, or pulse duration, refers to the time a single laser pulse takes from start to end. The range of pulse width variation varies greatly among different types of lasers. The pulse width determines the laser energy distribution over time and corresponds to the energy parameters in the EzCad software. In terms of processing effect, when the pulse width is small, the energy application range is small, but the energy density is high, giving the intuitive feeling that a larger power is used. Conversely, if the pulse width is large, the energy application range will correspondingly increase, while the energy density will decrease.
3. What's the FREQUENCY ?
Frequency refers to the number of pulses generated per second, for example, 30 KHz = 30000/second, which means 30000 pulses are generated per second. In the process of laser marking, the frequency will be directly reflected in the variation of the interval between each point. The lower the frequency, the farther the spacing, and the higher the frequency, the denser the point spacing.
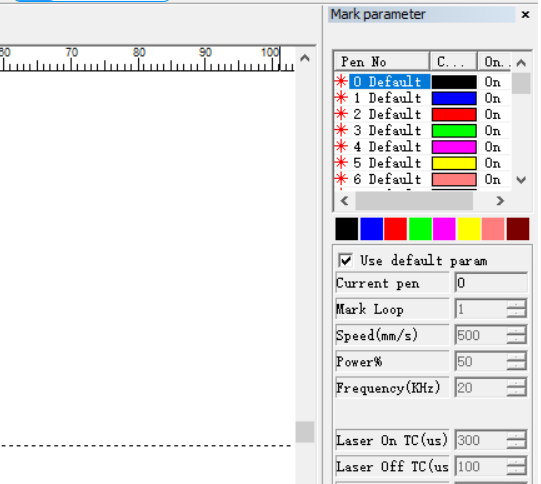
4. How to set the parameters ?
When debugging the laser engraving paramters, we need to adjust the spacing of the filling lines appropriately based on the characteristics of the current laser to ensure uniform energy distribution. The frequency and pulse width need to be adjusted according to the different materials, and there are no fixed parameters. It is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as the absorption efficiency and thermal stability of the material towards the laser.