The laser collimator is a critical optical component in laser welding systems. The core function is to convert the laser output beam with a certain divergence angle into a parallel beam. You can imagine it as the first step of a ‘beam shaper’, specifically responsible for straightening the laser.
1 What’s a Laser Collimator and How It Works in Laser Welding Machine?
1.1 The basic principle of laser collimator
The collimating lens is placed at the waist position of the laser output beam, which is the position of the thinnest point of the beam. According to the principles of geometric optics, a convex lens can convert the divergent light into parallel light. The output of a laser can be approximated as a “virtual point light source” with a certain divergence angle emitted from its waist. By adjusting the position of the lens, it is precisely adjusting the position of this “virtual point light source” relative to the focal point of the lens to achieve optimal collimation.
1.2 The role of laser collimator in laser welding system
- Control the beam divergence angle. The original beam output by fiber or CO2 lasers has a certain divergence angle. The beam is not perfectly parallel light, and it will diffuse with increasing propagation distance. The function of a collimator is to significantly reduce the divergence angle, keeping the beam nearly parallel over a considerable distance.
- Prepare for subsequent focus. The ideal input light for a focusing mirror is a parallel beam. Only when the light beam incident on the focusing mirror is parallel (or collimated), can it be accurately focused into a minimum, roundest, and highest energy density focal point. This is a prerequisite for achieving high-quality, deep penetration or precision welding.
- Ensure the quality of beam transmission. When the laser is transmitted from the laser to the laser welding head at a longer distance, the collimated beam can minimize energy loss and beam size changes during transmission. It will ensure stable beam characteristics received by the laser welding head.
1.3 The structure of a laser collimator
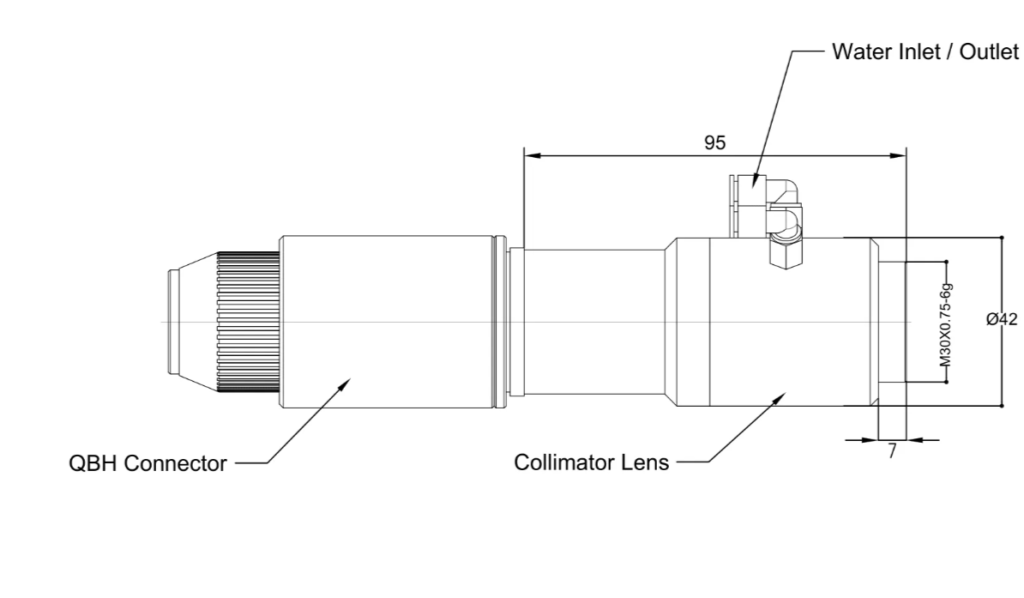
The core component of a laser collimator is the collimating lens, abbreviated as the lens.
According to the number of collimating lenses, laser collimator systems can be divided into single-lens systems and multi-lens systems. The single-lens system has a simple structure and is suitable for specific wavelengths. A multi-lens system is fit for high-power laser systems. It consists of multiple lens groups.
In addition to the lens, the laser collimator also requires a barrel and an adjustment device. The lens is precisely installed inside the metal barrel. The lens barrel is usually equipped with adjustment rings, top screws, and other adjustment devices to precisely adjust the position of the lens moving along the optical axis direction, in order to achieve the best collimation effect. In addition, high-power collimators require effective cooling design to reduce the impact of laser heating on the lens.
2 What is the difference between collimating lens and focusing lens?
Collimator lens: Convert scattered light into parallel light. Usually located near the output end of the laser or the front end of the beam transmission path.
Focusing lens: Concentrates parallel light into a small focal point. Usually located at the end of the processing head, closest to the workpiece.
3 How to choose the heat dissipation method of laser collimator?
In laser welding systems, the cooling method of the laser collimator is a key design to ensure its stable operation in high-power laser environments. The collimating lens absorbs some of the laser energy and converts it into heat. Insufficient heat dissipation can cause the refractive index of the lens to change with temperature, deformation of the lens, and even damage to the coating, ultimately resulting in beam quality degradation and equipment damage. There are two designs for cooling fiber laser collimators: an air-cooling design and a water-cooling design.
One is an Air-cooling design. It uses a fan to perform convective heat dissipation on the collimator housing. The laser collimator based on air cooling has a simple structure, low device cost, no water connection, and no risk of water leakage. Generally applicable to laser welding machines with power<2000W.
Another is a water-cooled design, which integrates a closed cooling water channel inside the collimator tube. Through the circulation of cooling water flow, it passes through the lens installation area and directly takes away heat. The laser collimator based on water cooling requires an external chiller, water pump, and pipeline, and there is a certain degree of water leakage and wind testing. Generally applicable to laser welding systems with a power greater than 2000W.
4 How to choose a cooling method for a laser welding machine
Here are some suggestions based on the laser power:
- Laser energy<1000W: Air cooling is the preferred option because it is designed to be lightweight and cost-effective.
- Laser energy of 1000W~6kW: Water cooling must be used, which is the mainstream configuration for industrial welding.
- Laser energy>6kW ultra-high peak power: A customized enhanced water cooling system is required, such as increasing flow/pressure.

5 Conclution
Laser collimator is an indispensable “beam parallelization tool” in laser welding systems. It receives the original divergent beam emitted by the laser and converts it into a high-quality parallel beam. It lays a solid foundation for subsequent precise focusing and efficient welding. Its performance and adjustment accuracy have a decisive impact on the processing capability and quality of the entire welding system. Choosing a collimator with appropriate focal length, high quality, good cooling, and easy precision adjustment is important for building high-performance laser welding systems.